Femtosecond laser is often used to gently and safely breakup hardened cataract to improve vision and minimize use of glasses. The laser pulse takes less than a femtosecond (one millionth of one billionth of a second) per pulse and the molecular breakup is very safe.
A cataract is the clouding of the natural lens that leads to blurry vision even with glasses, contact lenses or even after prior successful LASIK surgery.
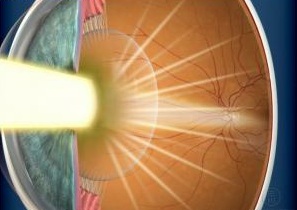
Crystalline lens inside an eye is working together with the cornea surface to bend the light and focus the picture on the retina. Young natural human lens is able to contract and expand to focus on close and distant objects giving us full range of vision. When the combination of the lens and cornea is not appropriate to focus the light on the retina precisely, vision becomes blurry and foggy.
Natural human lens becomes progressively harder and cloudier with age, more notable after 40. The clouding in the lens disrupts transmission of light through the lens. Vision may be blurred, dark, and distorted. Laser and ultrasound can be used to break it up and remove it during a surgical procedure known as cataract extraction or phacoemulsification. An artificial lens is then inserted to replace the darkened cataract and to focus the image clearly on the retina. Proper intraocular lens helps to see far and at reading distances even without glasses.
